
BNPL as Embedded Finance: Key Considerations for a Future Where Everyone Is a Lender
Financial services landscape is experiencing a revolutionary transformation where traditional boundaries between commerce and finance are dissolving. Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) as embedded finance represents more than just a payment innovation—it's reshaping the fundamental architecture of how financial services are delivered and consumed.
This convergence is creating an ecosystem where virtually any platform can become a financial services provider, democratizing lending and opening unprecedented opportunities for businesses across industries. As we move toward a future where everyone can be a lender, understanding the mechanics, opportunities, and challenges of embedded BNPL becomes crucial for businesses seeking to capitalize on this $7 trillion market opportunity.This convergence is creating an ecosystem where virtually any platform can become a financial services provider, democratizing lending and opening unprecedented opportunities for businesses across industries. As we move toward a future where everyone can be a lender, understanding the mechanics, opportunities, and challenges of embedded BNPL becomes crucial for businesses seeking to capitalize on this $7 trillion market opportunity.
What is Embedded Finance & BNPL?
Embedded finance occurs when financial services are seamlessly integrated within non-financial services and platforms. Think banking services within ridesharing applications, insurance services embedded in e-commerce transactions, or lending options appearing naturally at the point of purchase. This integration eliminates the friction of redirecting customers to external financial platforms, creating a native experience that feels like a natural part of the customer journey.
Embedded finance provides non-financial organizations with opportunities to seamlessly integrate payment, lending, and insurance into their products and services. Along with profitability increases, embedded finance substantially improves customer experience and customer loyalty by removing barriers between intention and action.
Embedded approach transforms financial services from standalone products into infrastructure that powers commerce, creating value for consumers, merchants, and financial service providers simultaneously.
BNPL: Gateway to Embedded Lending
Buy Now, Pay Later represents one of the most successful implementations of embedded finance. BNPL solutions allow consumers to purchase goods or services immediately and pay for them over time through installment plans, typically without traditional credit checks or interest charges for short-term arrangements. Unlike traditional credit cards or personal loans, BNPL is embedded directly at the point of sale, creating a seamless checkout experience. This integration eliminates friction in the purchasing process while providing consumers with flexible payment options that align with their cash flow preferences. BNPL model operates on several key principles:
- Instant approval: Decisions are made in real-time using alternative credit scoring methods
- Transparent terms: Clear payment schedules with minimal hidden fees
- Embedded integration: Seamlessly woven into the merchant's checkout process
- Risk distribution: Merchants and BNPL providers share transaction risks
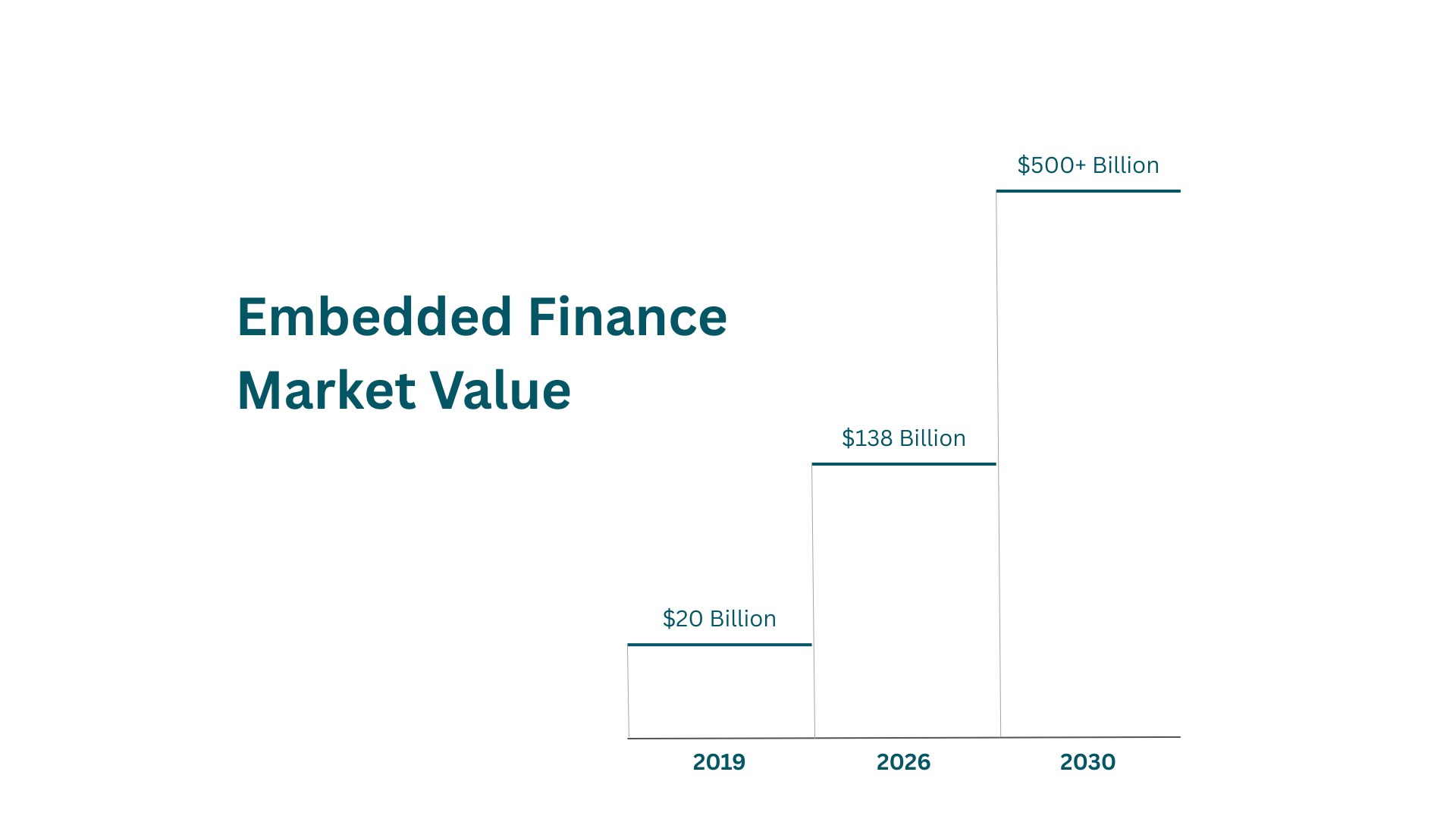
Embedded Finance & Embedded Lending (BNPL): Market Value
Embedded finance market has experienced explosive growth, with global market value reaching unprecedented levels. Industry analysts project the embedded finance market will exceed $500 trillion by 2030, representing a compound annual growth rate of over 32%. Within this ecosystem, embedded lending, particularly BNPL, accounts for a significant portion of the growth trajectory.
BNPL segment alone has demonstrated remarkable expansion, with transaction volumes growing from approximately $20 billion in 2019 to over $120 billion by 2024. This growth trajectory reflects fundamental shifts in consumer behavior, particularly among millennials and Generation Z consumers who prefer flexible payment options over traditional credit products.
Embedded finance creates value through multiple channels:
For Merchants
Integration of BNPL solutions typically increases average order values by 20-30% while improving conversion rates by 15-25%. The embedded nature reduces cart abandonment rates significantly, as customers can complete purchases without leaving the merchant's platform.
For Consumers
BNPL provides access to credit without the complexity of traditional loan applications. The transparent fee structure and interest-free short-term options appeal to cost-conscious consumers seeking budget management tools.
For Financial Service Providers
Embedded lending opens new customer acquisition channels while reducing customer acquisition costs. The data generated through embedded transactions provides valuable insights for risk assessment and product development.
North America leads the embedded finance market, driven by advanced fintech infrastructure and high consumer adoption rates. Europe follows closely, with strong regulatory frameworks supporting innovation while ensuring consumer protection. The Asia-Pacific region shows the highest growth potential, fueled by digital transformation initiatives and underserved populations seeking financial inclusion.
What's the Place of Banks, NBFCs & Fintechs in Embedded Finance and BNPL?
Traditional banks are repositioning themselves within the embedded finance ecosystem, leveraging their regulatory advantages and capital reserves. Many banks are developing Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) platforms that enable fintech companies and merchants to offer embedded financial products while the bank handles compliance and risk management.
Banks bring several advantages to embedded finance:
Regulatory expertise
Deep understanding of compliance requirements across jurisdictions
Capital availability
Substantial funding capacity for lending operations
Trust & credibility
Established consumer confidence in traditional banking institutions
Infrastructure stability
Robust systems capable of handling high transaction volumes
However, banks face challenges in agility and customer experience innovation, often requiring partnerships with more nimble fintech providers to deliver competitive embedded solutions.
Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs): Specialized Solutions
NBFCs occupy a unique position in the embedded finance ecosystem, offering specialized lending products with greater flexibility than traditional banks. These institutions often focus on specific market segments or product categories, developing deep expertise in particular lending niches.
NBFCs contribute through:
Specialized risk assessment
Tailored underwriting models for specific industries or demographics
Rapid product development
Faster iteration cycles for new financial products
Regulatory agility
More streamlined compliance processes for specific lending categories
Partnership flexibility
Easier integration with technology platforms and merchant partners
Fintech Companies: Innovation Catalysts
Fintech companies serve as the primary innovation drivers in embedded finance, developing the technology infrastructure and user experiences that make seamless financial integration possible. These companies typically focus on specific aspects of the embedded finance stack, from payment processing to risk assessment algorithms.
Fintech contributions include:
Technology innovation
Advanced APIs, machine learning algorithms, and user interface design
Rapid deployment
Faster time-to-market for new embedded finance solutions
Customer experience optimization
Focus on user-centric design and conversion optimization
Data analytics
Sophisticated tools for transaction analysis and risk management
The most successful embedded finance ecosystems involve collaboration between all three types of institutions, each contributing their core competencies to create comprehensive solutions.
Buy Now Pay Later - Embedded Finance Solution
Book a personal demo tour to explore our fintech powers.
Learn MoreHow Does Buy Now Pay Later Work?
BNPL systems operate through sophisticated technology stacks that enable real-time decision making and seamless user experiences. The process begins when a consumer selects BNPL as a payment option during checkout. Behind the scenes, multiple systems collaborate to assess creditworthiness, approve transactions, and establish payment schedules.
Credit Assessment Process
Modern BNPL platforms utilize alternative credit scoring methodologies that go beyond traditional credit reports. These systems analyze:
Transactional Data:
Purchase history, spending patterns, and payment behavior across multiple platforms provide insights into consumer financial habits.Digital Footprint Analysis:
Social media activity, device information, and online behavior patterns contribute to risk assessment models.Real-Time Verification:
Income verification through bank account analysis, employment verification, and identity confirmation occur within seconds of application.Machine Learning Models:
Advanced algorithms continuously learn from transaction outcomes, refining risk assessment accuracy over time.
Payment Processing Workflow
BNPL transaction process typically follows this sequence:
Consumer Selection:
Customer chooses BNPL option at checkoutInstant Assessment:
Real-time creditworthiness evaluation using alternative data sourcesApproval Decision:
Automated approval or decline within secondsPayment Collection:
Initial payment (typically 25%) processed immediatelyInstallment Setup:
Automated payment schedule established for remaining balanceOngoing Management:
Payment reminders, processing, and customer service
Risk Management Framework
Successful BNPL platforms implement comprehensive risk management strategies:
Dynamic Pricing:
Interest rates and fees adjust based on individual risk profiles and market conditions.Merchant Risk Sharing:
Partnerships with merchants often include risk-sharing arrangements to align incentives.Collection Strategies:
Automated payment processing with escalating collection procedures for delinquent accounts.Fraud Prevention:
Real-time fraud detection using machine learning and behavioral analysis.
World-Renowned Cases of Successful BNPL Implementation
Klarna: European Pioneer
Klarna, founded in Sweden in 2005, has become synonymous with BNPL innovation. The company's "Pay in 4" model allows consumers to split purchases into four equal payments over six weeks. Klarna's success stems from its focus on user experience and merchant integration.
Key Success Factors:
- Seamless checkout integration with over 450,000 merchants globally
- Strong brand recognition and consumer trust
- Comprehensive mobile application with shopping discovery features
- Strategic partnerships with major retailers including H&M, IKEA, and Sephora
Klarna's valuation peaked at $45.6 billion in 2021, demonstrating the market's confidence in the BNPL model's potential.
Afterpay: Revolutionizing Retail Finance
Australian-founded Afterpay transformed the retail landscape by making BNPL accessible to smaller merchants and younger consumers. The platform's "Pay in 4" model charges no interest to consumers, instead generating revenue through merchant fees.
Innovation Highlights:
- Zero-interest model attracting cost-conscious consumers
- Strong focus on millennial and Gen Z demographics
- Successful expansion into North American and European markets
- Integration with major platforms including Shopify and Square
Afterpay's acquisition by Square (now Block) for $29 billion in 2021 validated the strategic importance of embedded lending in the broader payments ecosystem.
Affirm: Enterprise-Focused Solutions
Affirm has distinguished itself by focusing on larger purchase amounts and longer-term installment plans. The company's approach emphasizes transparency and responsible lending practices.
Distinctive Features:
- Flexible repayment terms ranging from 3 to 48 months
- Clear interest rate disclosure and no hidden fees
- Strong enterprise partnerships with retailers like Peloton and Shopify
- Advanced underwriting using real-time data analysis
PayPal Pay in 4: Leveraging Existing Infrastructure
PayPal's entry into BNPL leveraged its existing merchant network and consumer base to rapidly scale its Pay in 4 offering. This demonstrates how established payment providers can successfully enter the embedded lending space.
Strategic Advantages:
- Instant access to 400+ million active users
- Existing merchant relationships across global markets
- Integrated ecosystem including Venmo and PayPal Credit
- Strong brand recognition and consumer trust
What Businesses Should Know Before Entering the BNPL Market?
BNPL industry operates in an evolving regulatory environment that requires careful navigation. Businesses entering this space must understand jurisdiction-specific requirements and prepare for increasing regulatory scrutiny.
Key Regulatory Considerations:
Consumer Protection Laws:
BNPL providers must comply with fair lending practices, truth-in-lending disclosures, and consumer protection regulations. Different jurisdictions have varying requirements for fee transparency and collection practices.Licensing Requirements:
Depending on the jurisdiction and business model, BNPL providers may need money lending licenses, payment service provider licenses, or other financial service authorizations.Data Protection:
GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, and other data protection regulations require robust data handling and privacy protection measures.Anti-Money Laundering (AML):
Know Your Customer (KYC) and AML compliance requirements apply to BNPL providers, necessitating identity verification and transaction monitoring systems.
Technology Infrastructure Requirements
Successful BNPL implementation requires sophisticated technology infrastructure capable of handling high-volume, real-time transactions while maintaining security and reliability.
Core Technology Components:API Gateway Architecture:
Robust APIs that can handle merchant integrations, payment processing, and third-party service connections with minimal latency.Real-Time Decision Engines:
Machine learning platforms capable of processing credit decisions within milliseconds while continuously improving accuracy.Payment Processing Systems:
Secure payment infrastructure supporting multiple payment methods, automated collections, and dispute resolution.Customer Management Platforms:
Comprehensive systems for customer onboarding, account management, communication, and customer service.Data Analytics Infrastructure:
Advanced analytics capabilities for risk assessment, business intelligence, and regulatory reporting.
Risk Management Strategies
BNPL providers face unique risk challenges that require specialized management approaches:
Credit Risk Mitigation:
- Develop sophisticated alternative credit scoring models
- Implement dynamic spending limits based on consumer behavior
- Create early warning systems for payment difficulties
- Establish partnerships with credit bureaus for comprehensive risk assessment
Operational Risk Management:
- Implement robust fraud detection and prevention systems
- Develop business continuity plans for system outages or security breaches
- Create comprehensive vendor management programs
- Establish strong internal controls and audit procedures
Market Risk Considerations:
- Monitor economic indicators that may impact consumer spending and repayment capacity
- Develop stress testing scenarios for various economic conditions
- Create hedging strategies for interest rate and currency fluctuations
- Establish contingency funding sources for periods of economic uncertainty
Partnership Strategy Development
Success in embedded finance requires strategic partnerships across the value chain:
Merchant Partnerships:
Develop win-win relationships with retailers by demonstrating clear value propositions including increased sales, higher average order values, and improved customer retention.Technology Partnerships:
Collaborate with e-commerce platforms, point-of-sale providers, and payment processors to ensure seamless integration capabilities.Financial Institution Partnerships:
Partner with banks or NBFCs for funding, regulatory compliance, and risk sharing arrangements.Data & Analytics Partnerships:
Leverage third-party data providers for enhanced risk assessment and customer insights.
Customer Experience Optimization
Embedded nature of BNPL requires exceptional attention to user experience design:
Easy Integration:
BNPL options should feel native to the merchant's checkout process without requiring separate account creation or complex authentication procedures.Transparent Communication:
Clear disclosure of terms, payment schedules, and any applicable fees builds trust and reduces customer service inquiries.Mobile Optimization:
With increasing mobile commerce adoption, BNPL solutions must provide excellent mobile experiences across all device types.Customer Support:
Comprehensive support systems including chatbots, self-service portals, and human agents ensure positive customer experiences throughout the payment lifecycle.
Financial Planning & Sustainability
Entering the BNPL market requires substantial financial planning and sustainable business model development:
Funding Requirements:
BNPL providers need significant capital to fund consumer purchases while waiting for installment payments. This requires access to credit lines, securitization programs, or partnership arrangements with financial institutions.Unit Economics Optimization:
Successful BNPL businesses carefully balance merchant fees, consumer charges, operational costs, and credit losses to achieve sustainable profitability.Scalability Planning:
Growth strategies must consider the capital-intensive nature of lending operations and the need for proportional risk management capabilities.
Future Outlook: Democratization of Lending
Convergence of BNPL and embedded finance signals a future where lending capabilities become as ubiquitous as payment processing. This democratization of financial services will likely lead to increased competition, improved consumer choice, and continued innovation in financial technology.
Future of finance is embedded, and BNPL is leading the way toward a world where every platform has the potential to become a financial services provider. Success in this environment requires careful planning, strategic partnerships, and a commitment to responsible lending practices that benefit all stakeholders in the financial ecosystem.